Data connectors
With a data connector, data cables can be connected quickly and easily to a device, as well as being detachable. At LAPP, you will find the most common connector types such as M8, M12 or RJ45 and many more for connecting Ethernet cables, sensor/actuator and fieldbus cables and fibre optic cables. Whether for harsh industrial environments, structured building cabling, data centres or control cabinets.
What is a data connector?
A data cable WITHOUT a connector is only half the truth.
It is only with a data connector that a data cable can be quickly, conveniently and safely connected to a device. You know this from home: a network cable with an RJ45 connector can be connected to the LAN interface of your laptop in no time at all.
In industry too, the connectors should be fixed but still be detachable at any time. Quick and convenient separation of the connection plays a central role, as this is the only way to guarantee flexible installation of machines and systems directly at their place of use, easy repair and maintenance and generally better handling of all system components.
The data connector electrically connects the cores of a copper-based data cable or the fibres in a fibre optic cable to the device. This is done via the pins/contacts/fibre ends of the data connector with the pins/contacts/fibre connections of the device. Depending on the design, the connector housing protects the contact point against the ingress of dust or liquids, e.g. while also providing protection against mechanical impact and protecting users against electric shock.
Two data cables can also be connected to one another using a data connector.
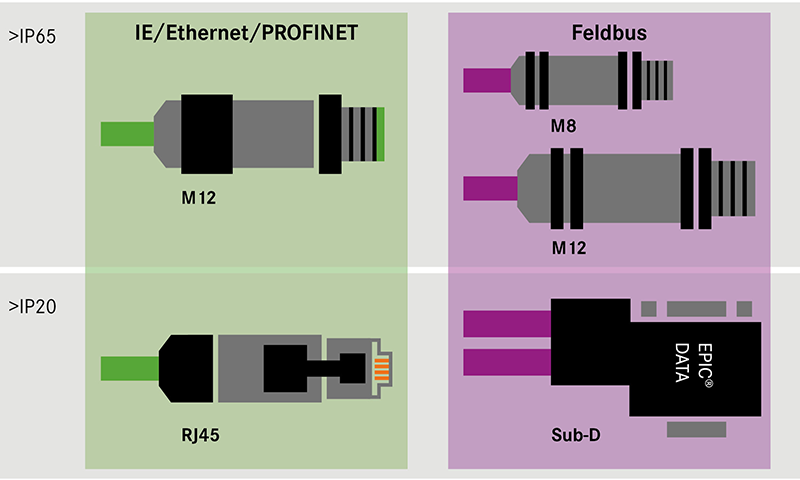
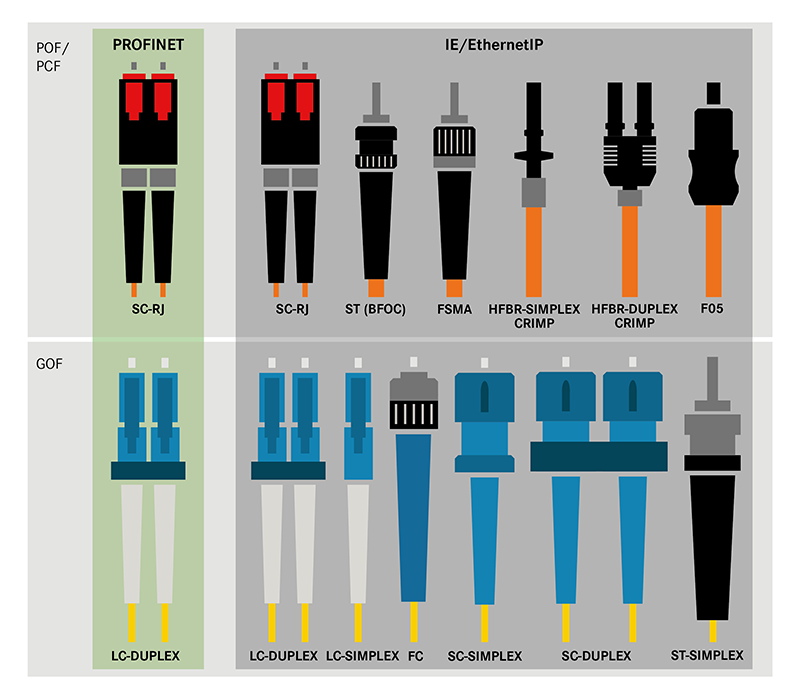
The most common data connectors are M8, M12, Sub-D, RJ45, ST(BFOC), FSMA, LC, FC, SC, ST-SC and SC-RJ.


Data transfer 3-2-1-GO!
In the LAPP product segment "Data Connectors" you will find connectors for independent on-site assembly of
Assembly
The connection of cables to connectors is referred to as assembly. If the assembly is produced ourselves, a decision must be made in advance on how the cable is to be connected to the connectors.
The connection technology to be used for the respective application depends on the location of the connector or cable, the processing location or application in the field, the design of the conductors to be connected, the availability of the tool and the costs for creating the connection. The most important connection types include screw connection, piercing technology (IPC), insulation displacement technology (IDC), locking clip and crimping.
During assembly, attention must also be paid to the colour coding inside the connector, which ensures that the cores of the cable are correctly connected to the connector.


What advantages does the use of self-configurable data connectors offer?
- The cable length can be determined very flexibly. This is advantageous if you do not know which cable length is required on site in advance.
- This saves space as you do not have to store any excess cables in the system. Your cable length always fits perfectly for your application.
- Choose the connector type and its properties based on your specific application.
- If you have enough data connectors and cables on site by the metre, you will remain independent of any delivery times and be able to act immediately.
Would you rather save time or do you prefer to completely eliminate any potential errors when assembling a data connection on site?
Did you know ?...
What actually is a data connector?
When used correctly, the term data connector, which is commonly used, actually only describes the male version of a data connector, but not the whole unit. A connector consists of a male part, the so-called plug, and a female part, the so-called socket.
The LAPP range of data connectors has both plugs and sockets ready for you.
What does field-configurable data connectors mean?
Thanks to their special design,field-configurable data connectors are suitable for assembly even under difficult conditions. This means that specialist staff can still reliably attach a connector to the cable without a workbench, under not ideal lighting and without special tools, e.g. standing on a ladder.
Which data connector should it be?
There are countless data connectors at LAPP (at least almost)!
To make choosing the right connector for your data cable a little easier, first consider the answers to the following two basic questions:
- For which challenge do you need a data connector?
- For connecting a data cable to a device.
- For connecting two data cables with the same transmission medium (extension function).
- For connecting two data cables with different transmission media (media coupler function).
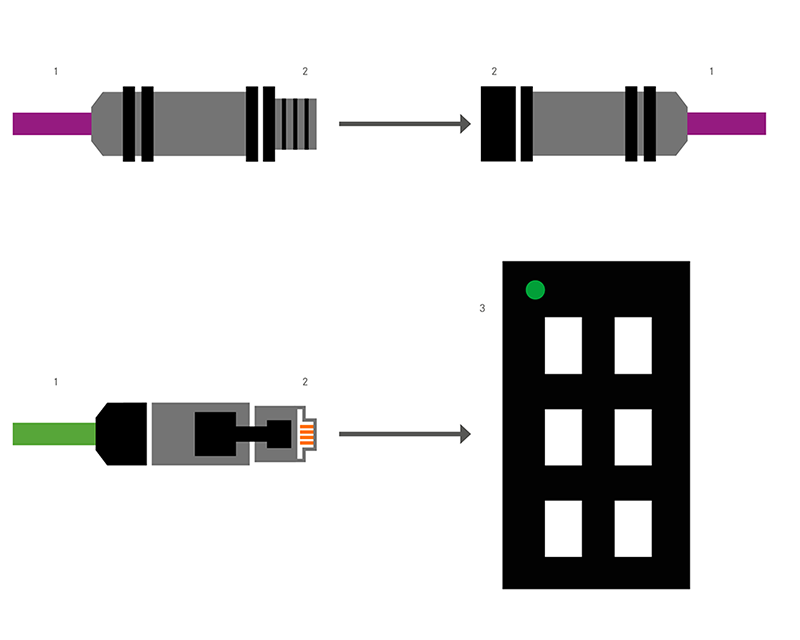

1. Transmission medium
2. Data connector
3. Device
For which transmission medium do you need a data connector?
- For copper cables.
- For fibre optic cables.
At LAPP, we divide the "data connectors" product segment into the following product groups:
Here you will find cable connectors for connecting, extending, repairing or routing Ethernet cables.
- Sensor/actuator connectors and Fieldbus connectors for copper-based data transmission
Data connectors from this product group are used for sensor/actuator wiring and support the PROFIBUS, CC-Link, CAN/DeviceNet, AS-Interface and other Fieldbus systems.
- Ethernet connectors for copper-based data transmission
Discover our data connectors for data transmission via Ethernet technology in shielded/unshielded version, with Industrial Ethernet or Profinet colour coding.
- Fibre optic connector for optical data transmission via fibre optic cables
LAPP offers fibre optic connectors for the fibre types of glass fibre (GOF), plastic fibre (POF) and plastic sheathed glass fibre (PCF).
- Media converter for connecting different transmission media
This type of data connector acts as a converter between two different transmission media. This means that media converters transfer data from one medium to another. Examples include copper to fibre optic cable, fibre optic cable to copper or fieldbus type A to fieldbus type B or similar.
Media converters ≠ Gateways!
Media converters must be technically separated from gateways.
Media converters enable the connection of different transmission media.
Gateways, on the other hand, do not change the transmission medium, but only the data transfer protocol. Incoming information is converted so that another network understands it.
How is a data connector constructed?
Connector Housing
The most important tasks of the housing are to ensure the mechanical stability of the connector, protect the electrical connection, ensure electrical shielding and ensure processability and environmental compatibility. Both plastics and metal alloys are used for the housing.
Contact area
The most important requirements for the detachable contact area are high electrical conductivity, high corrosion resistance and high mechanical wear resistance.
Due to their good electrical conductivity, copper or copper alloys are predominantly used for contact elements. Silver or gold surface coatings are often used to guarantee good corrosion protection.
Connector face
The shape of the surfaces to be combined in a connector housing is referred to as the connector face. For example, there are connectors with a round or rectangular connector face. If incorrect connectors are to be excluded, connector housings with different coding can be used. The coding is achieved using molded elements on the housings, such as nose or locking hooks.
Pin configuration
The arrangement and nature of the contacts in the connector are referred to as a pin configuration. Defined pin configurations ensure that only connectors of the same system can be plugged in. This prevents connectors for the power supply from being confused with data connectors, for example.
Where are data connectors required?
Do you use an industrial data cable? You need a data connector!
Regardless of whether your cable is fixed, flexible or exposed to dynamic movements, we at LAPP have the right data connector for you. For almost every conceivable application and industry.
As communication takes place at all levels, your data needs to master the path from the lowest sensor/actuator field level to the control level, right up to the company control level (MES/ERP), where a wired internet connection is made. And vice versa!
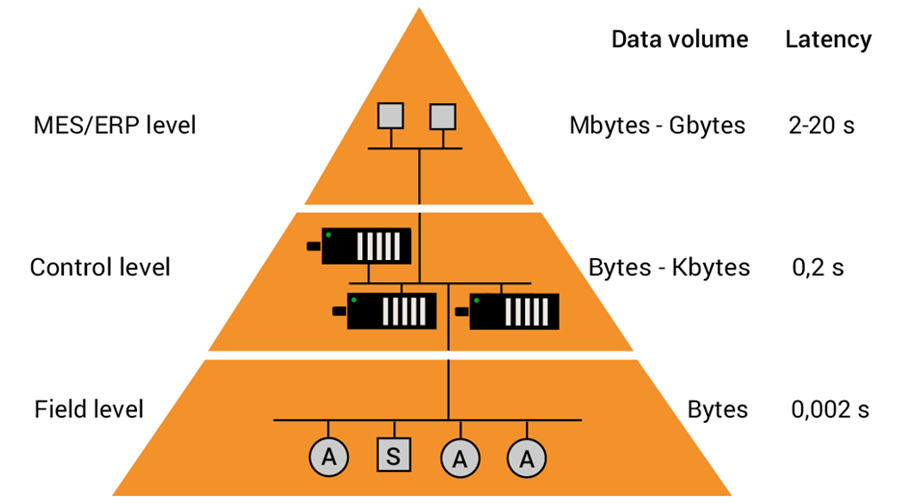

A manufacturing company can be depicted in the form of an automation pyramid with at least 3 levels, where all levels are interconnected by information technology: information exchange within one level is referred to as horizontal communication and information exchange between the levels is referred to as vertical communication.
Find out more here about the automation pyramid.
Which properties must a data connector fulfil?
It is not possible to say which properties the right data connector needs to have for you. Pay attention to these parameters
- Role
- Transfer medium
- Connector face
- Pole configuration
- Outer diameter of the cable to be connected
- Conductor cross-section of solid or braided conductor
- Shielding for stable data transmission in EMC-critical environments
- Cable outlet angle (35°, 90° and 180°)
- Resistances and IP protection class (UV, oil, water or similar)
- Vibration protection
Use our smart product filters to get to your top product in no time at all!

















